Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) stands as one of the most profound medical challenges of our time, affecting millions worldwide. Despite significant strides in research and treatment, AIDS continues to pose a formidable threat to public health. Understanding the complexities surrounding AIDS is crucial for fostering awareness, combatting stigma, and advancing efforts towards prevention and treatment.

What is Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) ?
- AIDS is a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
- HIV attacks the body's immune system, specifically targeting CD4 T cells, which play a vital role in orchestrating the body's defense against infections.
- As HIV progresses, it weakens the immune system, leaving the individual vulnerable to opportunistic infections and certain cancers.
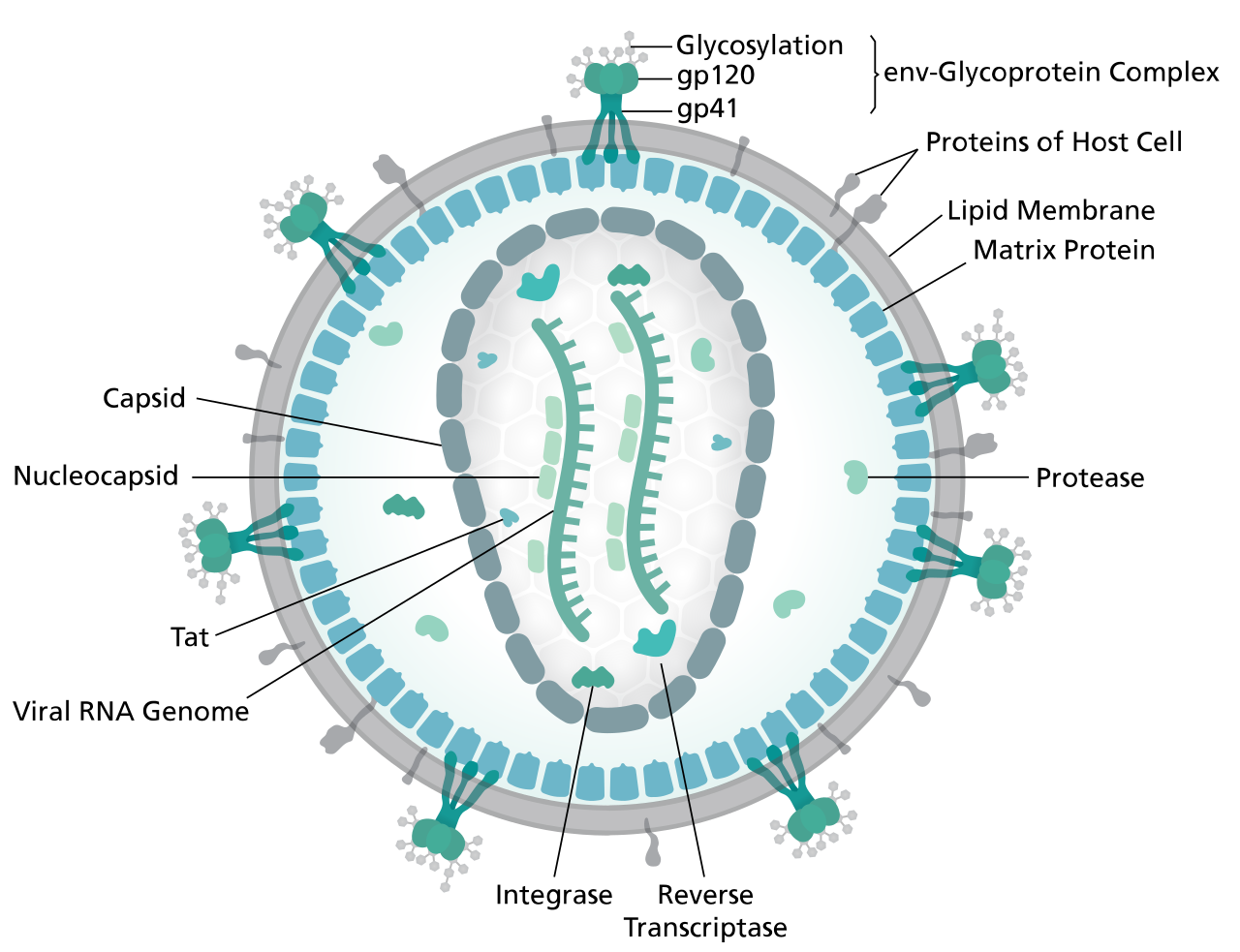
Diagram of the HIV Virion
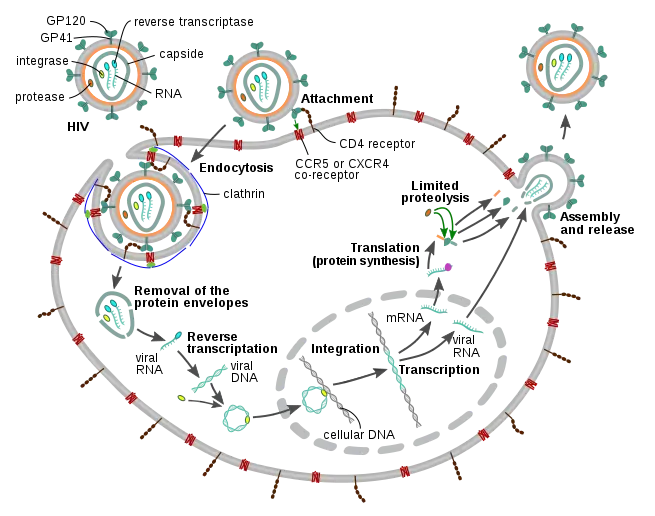
HIV transmission to AIDS
1- HIV Transmission: HIV is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing contaminated needles, or from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
2- Acute HIV Infection: After exposure to HIV, individuals may experience flu-like symptoms during the acute phase of infection. However, many people remain asymptomatic for years.
3- Chronic HIV Infection: Without treatment, HIV progresses to a chronic stage, characterized by persistent viral replication and gradual depletion of CD4 T cells.
4- AIDS Diagnosis: AIDS is diagnosed when HIV infection has progressed to a point where the immune system is severely compromised, as indicated by a low CD4 cell count or the presence of opportunistic infections or cancers.
Prevention strategies
Prevention strategies
Safe Sex Practices
Practicing safe sex, including consistent condom use and reducing the number of sexual partners, can significantly reduce the risk of HIV transmission.
Needle Exchange Programs
Providing access to sterile needles and syringes can reduce the transmission of HIV among individuals who inject drugs
HIV Testing and Counseling
Regular HIV testing, coupled with counseling on risk reduction strategies, is essential for early detection and intervention.
Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
PrEP involves taking antiretroviral medications to prevent HIV infection in individuals at high risk, such as serodiscordant couples or injection drug users.
Start writing here...
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)